Controlling Posterior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spurs are abnormal bony growths that develop at the back of or under the heel. Inflammation around a spur, more so than the spur itself, can cause significant pain. Fortunately, symptoms can be eased with non-surgical treatments for the vast majority of people.
Causes
When a bone is subjected to pressure, rubbing, or other stress over long periods, it tries to repair itself by building extra bone. This extra bone is what is referred to as a ?spur?. Many form as part of the aging process when cartilage breaks down in the joints.
Symptoms
You'll typically first notice early heel spur pain under your heel in the morning or after resting. Your heel pain will be worse with the first steps and improves with activity as it warms up. When you palpate the tender area you may feel a tender bony lump. As your plantar fasciitis deteriorates and your heel spur grows, the pain will be present more often.
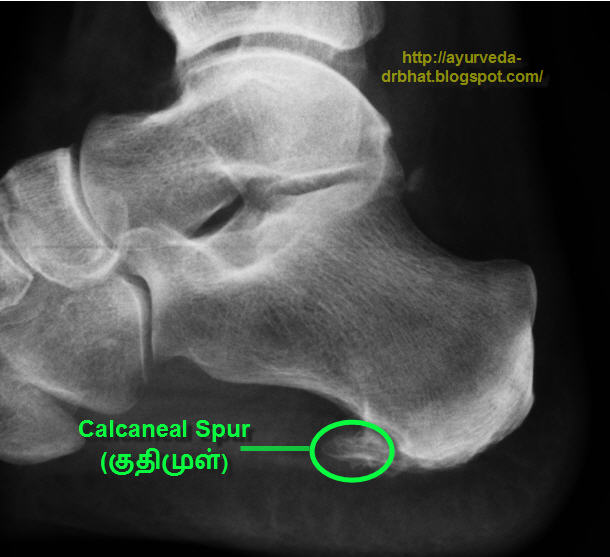
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a heel spur can be done with an x-ray, which will be able to reveal the bony spur. Normally, it occurs where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone. When the plantar fascia ligament is pulled excessively it begins to pull away from the heel bone. When this excessive pulling occurs, it causes the body to respond by depositing calcium in the injured area, resulting in the formation of the bone spur. The Plantar fascia ligament is a fibrous band of connective tissue running between the heel bone and the ball of the foot. This structure maintains the arch of the foot and distributes weight along the foot as we walk. However, due to the stress that this ligament must endure, it can easily become damaged which commonly occurs along with heel spurs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Elevation of the affected foot and leg at rest may diminish the pain. Applying gentle heat to the painful area may ease the pain by dilating local blood vessels. One also can protect the heel by placing a foam rubber pad in the heel of the shoe. A pad about one-half inch thick will raise the heel, shift the weight of the body forward, and protect the irritated muscles attached to the heel bone. The same effect can be achieved by using adhesive tape to turn the foot inward. Additional treatment may consist of a number of physical therapies, such as diathermy, ultrasound waves and whirlpool baths.
Surgical Treatment
In some cases, heel spurs are removed by surgery after an X-ray. While the surgery is typically effective, it?s a timely and expensive procedure. Even after surgery, heel spurs can re-form if the patient continues the lifestyle that led to the problem. These reasons are why most people who develop painful heel spurs begin looking for natural remedies for joint and bone pain. Surgery isn?t required to cure a heel spur. In fact, more than 90 percent of people get better with nonsurgical treatments. If nonsurgical methods fail to treat symptoms of heel spurs after 12 months, surgery may be necessary to alleviate pain and restore mobility.
Prevention
Heel Spur symptoms can be prevented from returning by wearing proper shoes and using customized orthotics and insoles to relieve pressure. It is important to perform your exercises to help keep your foot stretched and relaxed.